Increased Use of Telemedicine During the Pandemic
April 3, 2023

Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of telemedicine by physicians was minimal. New findings from the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) indicate that the pandemic increased the use of telemedicine for office-based physicians from 15 percent in 2018-2019 to 87 percent in 2021. Eighty percent of physicians plan to continue using telemedicine after the pandemic.
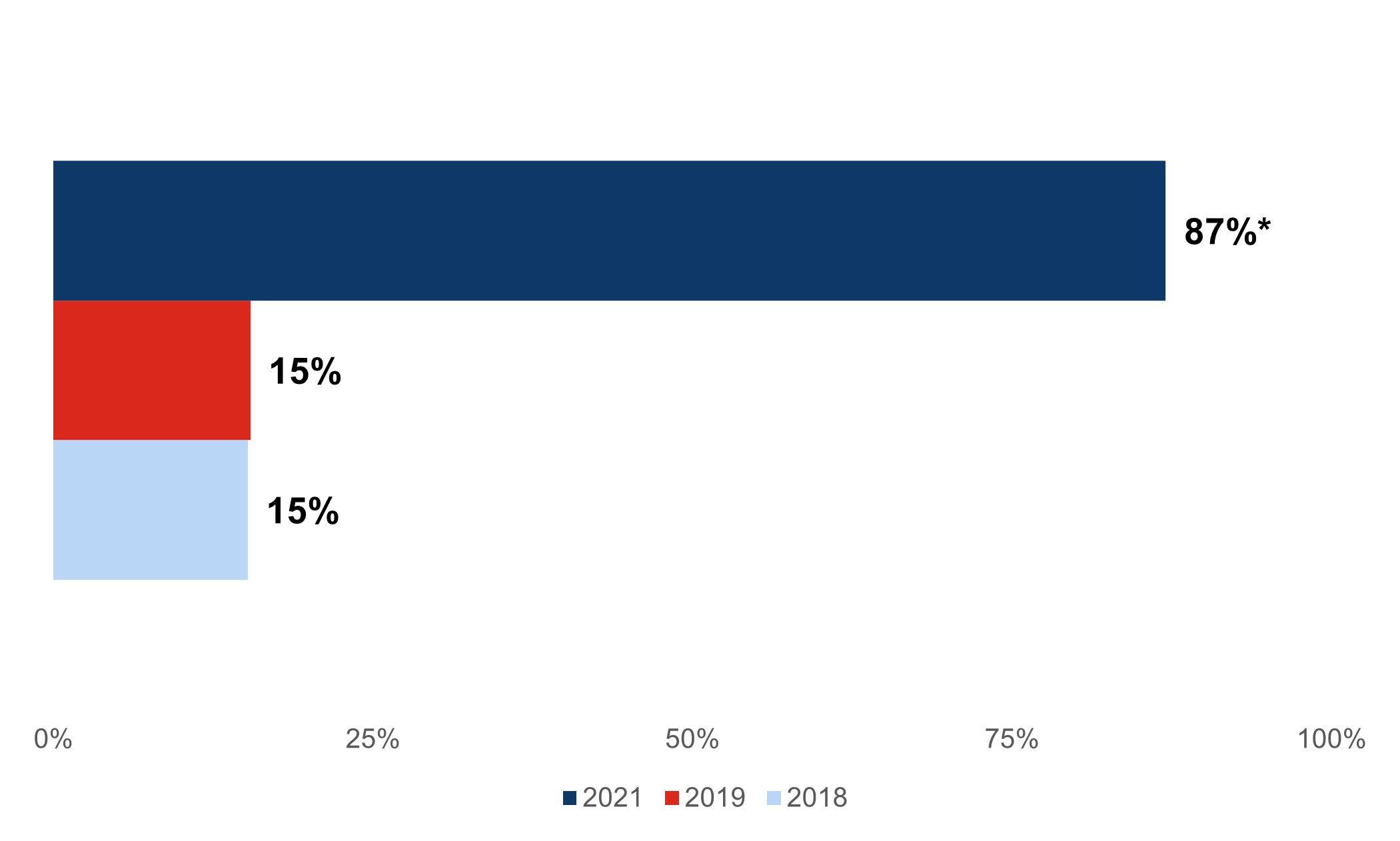
Figure 1: Percent of office-based physicians that used telemedicine, 2018-2021.
Source: National Electronic Health Record Survey, 2018-2021.
Key Findings:
- While only 15 percent of office-based physicians used any form of telemedicine in 2018-2019, its usage increased six times to 87 percent in 2021.
- Self-employed physicians were less likely to use telemedicine by at least 17 percentage points than larger practices (with more than three physicians).
- Physicians participating in payment models (patient centered medical home (PCMD, accountable care organizations (ACOs), or Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS)) were significantly more likely to use telemedicine than non-participants.
- Over 70 percent of physicians reported patients’ difficulty using telemedicine tools as the most common barrier to using telemedicine.
- Most physicians (62 percent) were fully or somewhat satisfied with their use of telemedicine.
Click here to read more of the ONC report.
Integrating Telehealth Apps with EHRs
The pandemic not only increased the use of telehealth but also increased the number of COVID-19-related apps. According to the American Journal of Managed Care, there were 87 telehealth-related apps created from March 2020 to June 2021 to support patient care during the pandemic. The findings indicate the growing potential of integrating telehealth apps with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to increase the accessibility and quality of health care for patients.
These apps supported the COVID-19 response efforts, such as secure messaging, vaccine administration, and laboratory testing. These telehealth and COVID-19-related apps were mainly used for administrative functions. Other common uses of these apps include patient education, health information management, provider efficiency tools, and digital check-in.
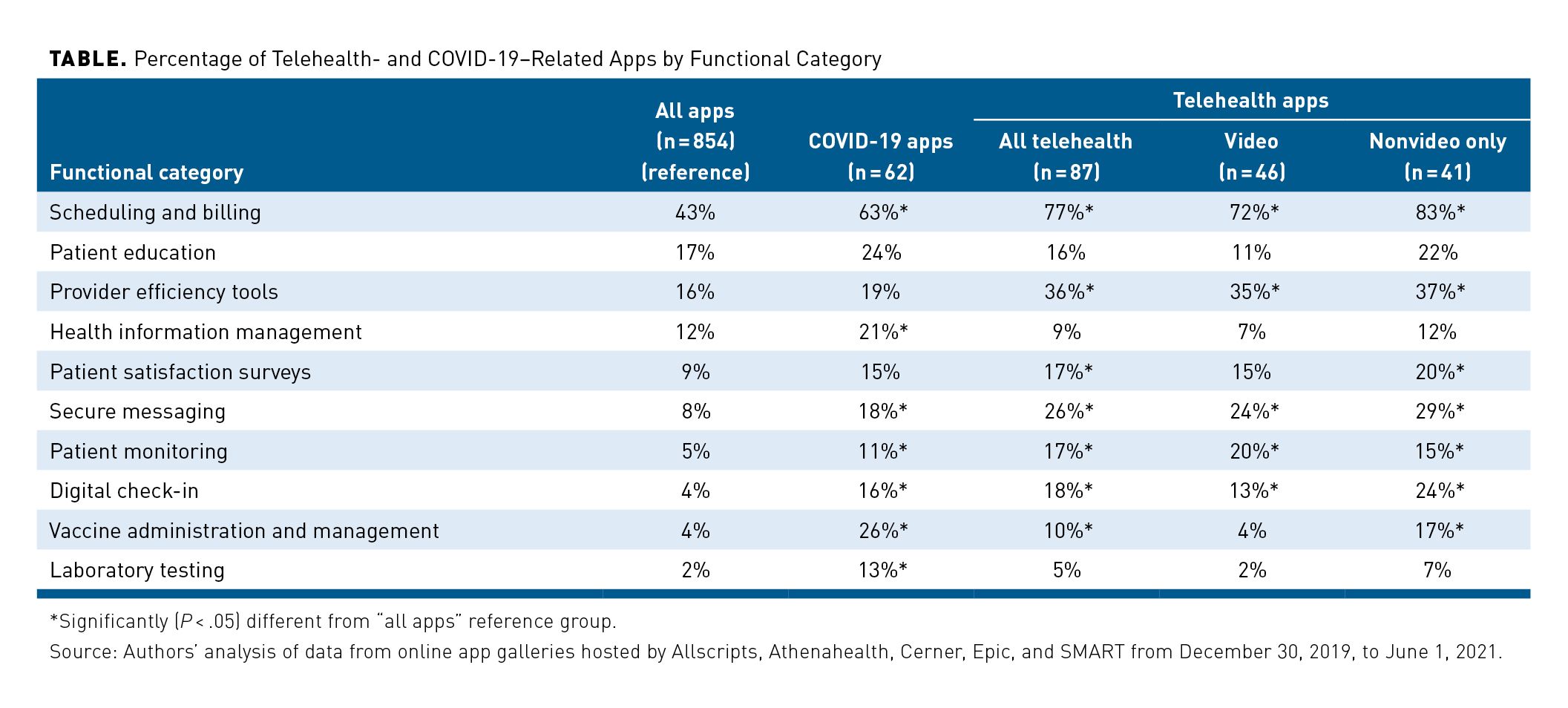
Key findings from the article:
- In May 2020, the federal government finalized a policy to make integrating third-party apps with electronic health records (EHRs) easier by requiring EHR developers to adopt secure, standards-based application programming interfaces.
- We observed a rapid increase in telehealth- and COVID-19–related apps integrating with EHRs following the onset of the pandemic.
- These apps provided healthcare providers with many new tools to diagnose, treat, and communicate with patients.
Click here to read more.